Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most common health problems, affecting people across all age groups. At Ray & Rio Clinic, we specialize in diagnosing and treating UTIs effectively, ensuring that our patients regain their comfort and well-being. Whether you’re experiencing a one-time infection or dealing with recurring issues, this comprehensive guide will provide the information you need to understand and manage the condition.
What Is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) occurs when bacteria enter the urinary system, causing inflammation and infection. This can happen in any part of the urinary tract, including the bladder, urethra, ureters, or kidneys. UTIs are typically caused by bacteria like Escherichia coli (E. coli), which naturally reside in the gut.
Left untreated, urinary tract infections (UTIs) can worsen and lead to serious complications such as kidney infections.
What Is the Urinary Tract?
The urinary tract is a system in the body responsible for removing waste and excess water. It consists of:
- Kidneys: Filter waste from the blood to produce urine.
- Ureters: Transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: Stores urine until it is expelled.
- Urethra: The tube through which urine exits the body.
Understanding how the urinary tract works is key to identifying issues like chronic urinary tract infection, which can result from disruptions in this system.
How Common Are Urinary Tract Infections?
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are extremely common, especially among women. Nearly half of all women will experience a UTI at some point in their lives. Men, while less frequently affected, can still develop UTIs, particularly as they age.
At Ray & Rio Clinic, we treat hundreds of patients every year with symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe infections.
What Are the Signs of a Urinary Tract Infection?
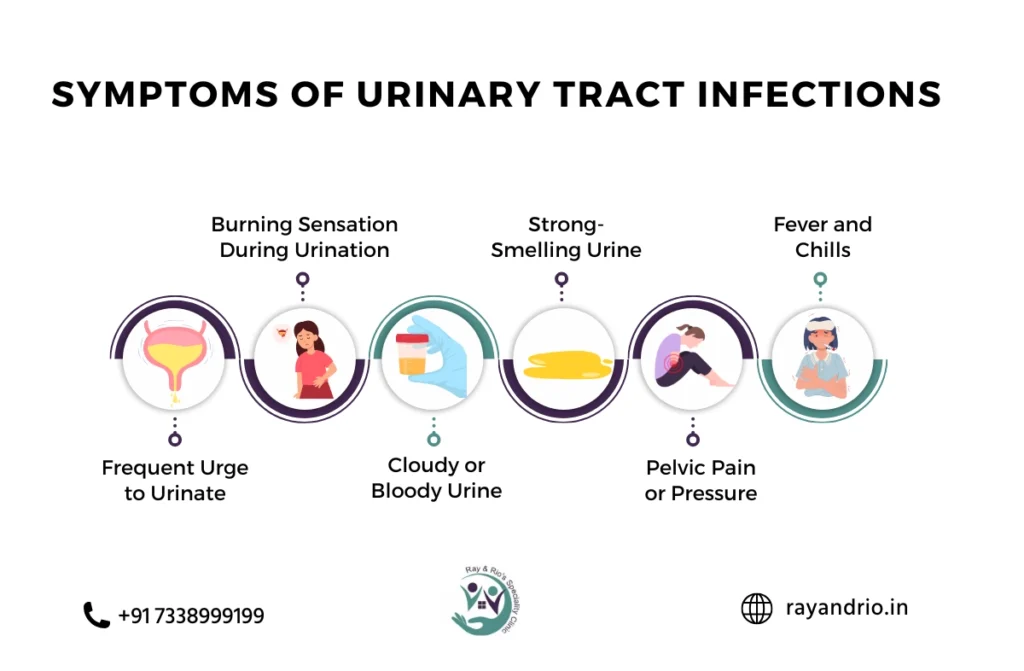
Recognizing the symptoms of urinary tract infections (UTIs) early can prevent complications:
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate.
- A burning sensation during urination.
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
- Lower abdominal pain or back pain.
For cases where a UTI comes back right after antibiotics, additional symptoms like fatigue or fever may indicate a deeper issue.
How Do You Get a Urinary Tract Infection?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) typically occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra.
- Hygiene practices: Improper wiping or infrequent cleaning can increase the risk.
- Sexual activity: This can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Medical devices: Catheters or other invasive devices may also cause infections.
Patients dealing with chronic urinary tract infections often have structural issues or underlying conditions that make them more prone to recurrent infections.
What Is the Major Cause of a Urinary Tract Infection?
The primary cause of urinary tract infections (UTIs) is E. coli, a bacterium found in the digestive system. Other bacteria, fungi, or viruses can occasionally be responsible, especially in complex or recurrent cases.
Certain risk factors, like diabetes or a weakened immune system, can increase the chances of developing a chronic urinary tract infection.
Who Is at the Greatest Risk of Getting a Urinary Tract Infection?
- Women: Due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria easier access to the bladder.
- Older adults: Aging increases the risk of UTIs due to changes in the urinary tract.
- People with medical conditions: Those with diabetes, kidney stones, or a suppressed immune system are more likely to experience infections.
For patients asking, “Can recurrent UTIs be a sign of cancer?”, we recommend prompt evaluation to rule out any serious underlying conditions.
What Tests Will Be Done to Diagnose a Urinary Tract Infection?
At Ray & Rio Clinic, we use a range of diagnostic tools to identify urinary tract infections (UTIs):
- Urinalysis: A test that checks for bacteria, white blood cells, or blood in the urine.
- Urine culture: Identifies the specific bacteria causing the infection.
- Imaging tests: Ultrasounds or CT scans may be used for recurrent or complex cases.
For patients with UTI comes back right after antibiotics, advanced diagnostics may be necessary to pinpoint the cause.
What Is the Best Thing to Do for a Urinary Tract Infection?
If you suspect you have a urinary tract infection (UTI):
- Stay hydrated: Drinking water helps flush bacteria from your system.
- Seek medical treatment: Antibiotics are typically required to clear the infection.
- Avoid irritants: Caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods can worsen symptoms.
When dealing with a chronic urinary tract infection, lifestyle changes and long-term care plans may be needed.
What Are the Symptoms of a Chronic Urinary Tract Infection?
A chronic urinary tract infection often presents with persistent or recurring symptoms:
- Pain or burning during urination that doesn’t fully resolve.
- Frequent urges to urinate, even shortly after voiding.
- Persistent lower abdominal discomfort.
At Ray & Rio Clinic, we provide comprehensive care to manage and treat chronic cases effectively.
What Are the Causes of Chronic Urinary Tract Infections?
- Incomplete treatment: When an initial infection isn’t fully eradicated.
- Structural issues: Abnormalities in the urinary tract can trap bacteria.
- Underlying conditions: Diabetes, kidney stones, or bladder issues can increase susceptibility.
Patients with a UTI comes back right after antibiotics often have one or more of these contributing factors.
What Increases Your Risk of Chronic Urinary Tract Infections?
- Frequent antibiotic use: This can disrupt the balance of good and bad bacteria.
- Hormonal changes: Especially during menopause, which can affect the urinary tract lining.
- Medical devices: Long-term catheter use significantly raises the risk.
If you’re wondering, “Can recurrent UTIs be a sign of cancer?”, persistent infections should be evaluated to rule out malignancies.
How Is a Chronic Urinary Tract Infection Treated?
Treating a chronic urinary tract infection involves:
- Antibiotics: Long-term, low-dose regimens may be prescribed.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Including increased hydration and improved hygiene practices.
- Medical procedures: Addressing any structural or functional abnormalities in the urinary tract.
At Ray & Rio Clinic, our personalized care ensures effective treatment plans tailored to each patient’s needs.
How Can I Prevent a Chronic Urinary Tract Infection?
Preventing chronic urinary tract infections requires proactive measures:
- Drink water regularly: Staying hydrated flushes out bacteria.
- Practice hygiene: Always wipe front to back after using the restroom.
- Urinate after sexual activity: This helps reduce bacterial entry into the urinary tract.

UTI Comes Back Right After Antibiotics
It’s frustrating when a UTI comes back right after antibiotics. This may be due to antibiotic resistance or incomplete treatment.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully to ensure the infection is fully treated.
- Consult with specialists like those at Ray & Rio Clinic for alternative treatments or further evaluation.
What Are Recurrent UTIs?
Recurrent UTIs are infections that occur frequently, often within weeks of treatment.
- They may signal an unresolved issue, such as a structural problem or underlying condition.
- For patients asking, “Can recurrent UTIs be a sign of cancer?”, ongoing infections require medical attention to rule out serious causes.
Can Recurrent UTIs Be a Sign of Cancer?
While rare, recurrent UTIs can sometimes indicate bladder or kidney cancer.
- Early symptoms may mimic those of common UTIs, such as blood in the urine.
- At Ray & Rio Clinic, we provide thorough evaluations to ensure accurate diagnoses and peace of mind.
Conclusion
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can disrupt daily life, but with expert care from Ray & Rio Clinic, you can find relief and prevent future infections. Whether you’re dealing with an initial infection or seeking answers to questions like “Can recurrent UTIs be a sign of cancer?”, our team is here to help.
Read Also : Gallbladder Removal Side Effects

